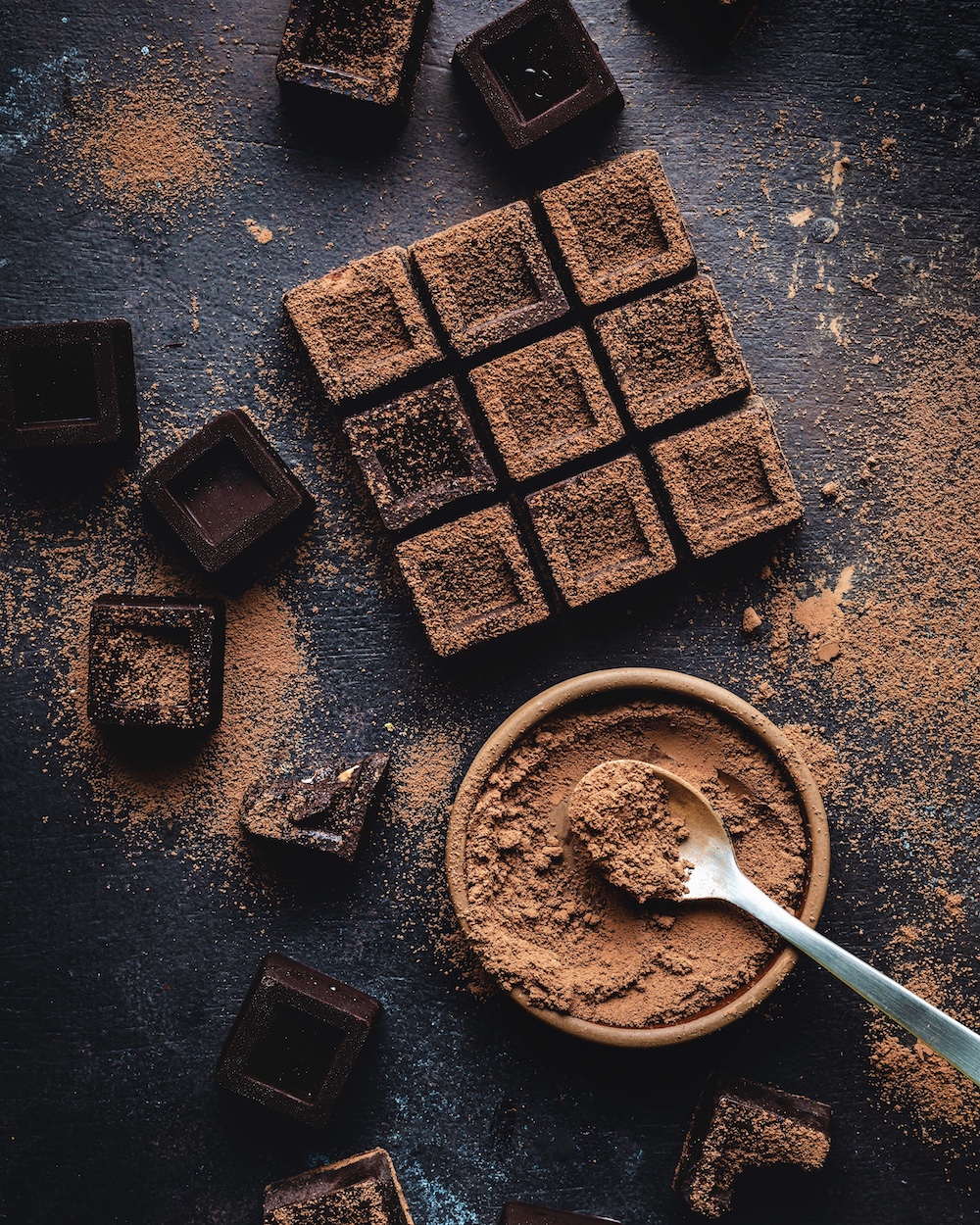
What is
Bitter Chocolate?
Bitter chocolate is a type of chocolate that contains a high percentage of cocoa solids and cocoa butter but minimal sugar. It is often used in baking and cooking to add a deep, rich chocolate flavor without the overwhelming sweetness of regular dark chocolate.
Origins & History
Bitter chocolate has roots in ancient Mesoamerican cultures, where cacao was revered and used in various forms. The Aztecs and Mayans consumed a beverage made from crushed cacao beans, often flavored with spices, which was far less sweet than modern chocolate. Over time, as chocolate technology evolved in Europe, the darker, less sweet forms of chocolate became popular among culinary artisans.
Taste & Texture
Bitter chocolate offers a deep, rich, and intense chocolate flavor, typically with pronounced bitterness and a slightly earthy undertone that balances out its richness.
Ingredients
Cocoa Solids
The non-fat component of the cocoa bean that comprises the flavor and color of chocolate.
Cocoa Butter
A natural fat extracted from the cocoa bean, responsible for the smooth texture and mouthfeel of chocolate.

Sugar
Used sparingly in bitter chocolate, sugar balances the intense cocoa flavor but is present in significantly lower amounts compared to regular chocolate.
Emulsifiers (optional)
Ingredients like soy lecithin that may be added to improve texture and stability, though many high-quality bitter chocolates do not contain them.

Images may not reflect the actual item.
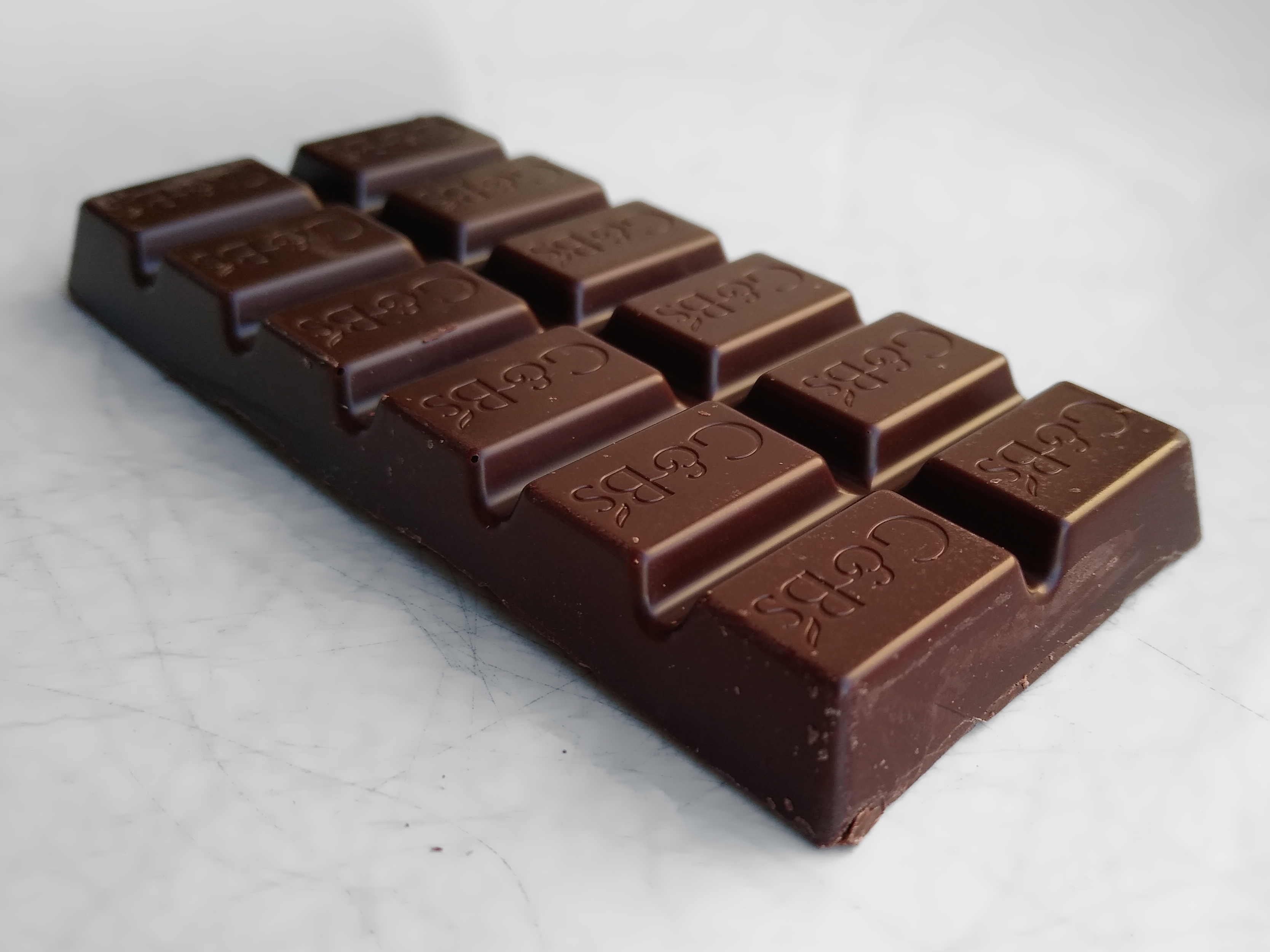








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/faw-detail-k-m-85-percent-hacienda-victoria-ecuador-rkilgore-1316-1-97780e8a8211466db27a7915125a89c6.jpeg)